Android MediaMuxer+MediaCodec 编码yuv数据成mp4
本文共 9010 字,大约阅读时间需要 30 分钟。
一、简介
使用 MediaCodec 对 yuv 数据进行编码,编码的格式为 H.264(AVC) 。
使用 MediaMuxer 将视频track和音频track混合到 mp4 容器中,通常视频编码使用H.264(AVC)编码,音频编码使用AAC编码。二、流程分析
(简要介绍一下流程,具体api的参数说明起来篇幅太大,不清楚的可以自己搜索一下)
- 创建编码器并配置
MediaFormat mediaFormat = MediaFormat.createVideoFormat(MediaFormat.MIMETYPE_VIDEO_AVC, videoWidth, videoHeight);// 设置编码的颜色格式,实则为nv12(不同手机可能会不一样)mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_COLOR_FORMAT, MediaCodecInfo.CodecCapabilities.COLOR_FormatYUV420Flexible);// 设置视频的比特率,比特率太小会影响编码的视频质量mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_BIT_RATE, width * height * 6);// 设置视频的帧率mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_FRAME_RATE, 30);// 设置I帧(关键帧)的间隔时间,单位秒mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_I_FRAME_INTERVAL, 1);// 创建编码器、配置和启动MediaCodec encoder = MediaCodec.createEncoderByType(MediaFormat.MIMETYPE_VIDEO_AVC);encoder.configure(mediaFormat, null, null, MediaCodec.CONFIGURE_FLAG_ENCODE);encoder.start();
关于比特率可以参考:
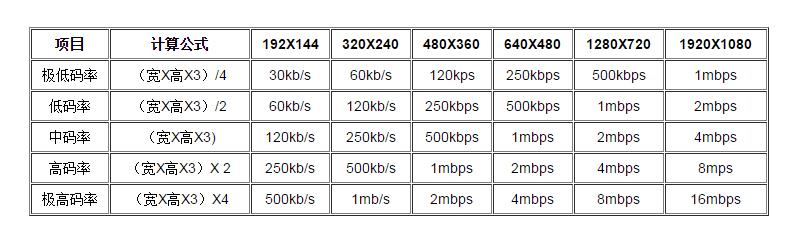
- 编码一帧数据
private void encode(byte[] yuv, long presentationTimeUs) { // 一、给编码器设置一帧输入数据 // 1.获取一个可用的输入buffer,最大等待时长为DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_US int inputBufferIndex = mEncoder.dequeueInputBuffer(DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_US); ByteBuffer inputBuffer = mEncoder.getInputBuffer(inputBufferIndex); // 2.将输入数据放到buffer中 inputBuffer.put(yuv); // 3.将buffer压入解码队列中,即编码线程就会处理队列中的数据了 mEncoder.queueInputBuffer(inputBufferIndex, 0, yuv.length, presentationTimeUs, 0); // 二、从编码器中取出一帧编码后的输出数据 // 1.获取一个可用的输出buffer,最大等待时长为DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_US MediaCodec.BufferInfo bufferInfo = new MediaCodec.BufferInfo(); int outputBufferIndex = mEncoder.dequeueOutputBuffer(bufferInfo, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_US); ByteBuffer outputBuffer = mEncoder.getOutputBuffer(outputBufferIndex); // 2.TODO MediaMuxer将编码数据写入到mp4中 // 3.用完后释放这个输出buffer mEncoder.releaseOutputBuffer(outputBufferIndex, false);} - MediaMuxer写入编码数据 在写入前,需要配置一些视频的头部信息(csd参数),否则会报错。csd参数全称Codec-specific Data。对于H.264来说,"csd-0"和"csd-1"分别对应sps和pps;对于AAC来说,"csd-0"对应ADTS。
// 写入头部信息,并启动 MediaMuxerprivate int writeHeadInfo(ByteBuffer outputBuffer, MediaCodec.BufferInfo bufferInfo) { byte[] csd = new byte[bufferInfo.size]; outputBuffer.limit(bufferInfo.offset + bufferInfo.size); outputBuffer.position(bufferInfo.offset); outputBuffer.get(csd); ByteBuffer sps = null; ByteBuffer pps = null; for (int i = bufferInfo.size - 1; i > 3; i--) { if (csd[i] == 1 && csd[i - 1] == 0 && csd[i - 2] == 0 && csd[i - 3] == 0) { sps = ByteBuffer.allocate(i - 3); pps = ByteBuffer.allocate(bufferInfo.size - (i - 3)); sps.put(csd, 0, i - 3).position(0); pps.put(csd, i - 3, bufferInfo.size - (i - 3)).position(0); } } MediaFormat outputFormat = mEncoder.getOutputFormat(); if (sps != null && pps != null) { outputFormat.setByteBuffer("csd-0", sps); outputFormat.setByteBuffer("csd-1", pps); } int videoTrackIndex = mMediaMuxer.addTrack(outputFormat); Log.d(TAG, "videoTrackIndex: " + videoTrackIndex); mMediaMuxer.start(); return videoTrackIndex;}// 写入一帧编码后的数据mMediaMuxer.writeSampleData(mVideoTrackIndex, outputBuffer, bufferInfo); - 结束后释放相应对象
mEncoder.stop();mEncoder.release();mMediaMuxer.release();
三、完整代码
包含一些基本的返回值检查、接口回调、以及可以中途停止解码的方法等。
import android.media.MediaCodec;import android.media.MediaCodecInfo;import android.media.MediaFormat;import android.media.MediaMuxer;import android.util.Log;import java.io.IOException;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;public class VideoEncoder { private static final String TAG = "VideoEncoder"; private final static String MIME_TYPE = MediaFormat.MIMETYPE_VIDEO_AVC; private static final long DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_US = 10000; private MediaCodec mEncoder; private MediaMuxer mMediaMuxer; private int mVideoTrackIndex; private boolean mStop = false; public void init(String outPath, int width, int height) { try { mStop = false; mVideoTrackIndex = -1; mMediaMuxer = new MediaMuxer(outPath, MediaMuxer.OutputFormat.MUXER_OUTPUT_MPEG_4); mEncoder = MediaCodec.createEncoderByType(MIME_TYPE); MediaFormat mediaFormat = MediaFormat.createVideoFormat(MIME_TYPE, width, height); // 编码器输入是NV12格式 mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_COLOR_FORMAT, MediaCodecInfo.CodecCapabilities.COLOR_FormatYUV420Flexible); mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_BIT_RATE, width * height * 6); mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_FRAME_RATE, 30); mediaFormat.setInteger(MediaFormat.KEY_I_FRAME_INTERVAL, 1); mEncoder.configure(mediaFormat, null, null, MediaCodec.CONFIGURE_FLAG_ENCODE); mEncoder.start(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void release() { mStop = true; if (mEncoder != null) { mEncoder.stop(); mEncoder.release(); mEncoder = null; } if (mMediaMuxer != null) { mMediaMuxer.release(); mMediaMuxer = null; } } public void encode(byte[] yuv, long presentationTimeUs) { if (mEncoder == null || mMediaMuxer == null) { Log.e(TAG, "mEncoder or mMediaMuxer is null"); return; } if (yuv == null) { Log.e(TAG, "input yuv data is null"); return; } int inputBufferIndex = mEncoder.dequeueInputBuffer(DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_US); Log.d(TAG, "inputBufferIndex: " + inputBufferIndex); if (inputBufferIndex == -1) { Log.e(TAG, "no valid buffer available"); return; } ByteBuffer inputBuffer = mEncoder.getInputBuffer(inputBufferIndex); inputBuffer.put(yuv); mEncoder.queueInputBuffer(inputBufferIndex, 0, yuv.length, presentationTimeUs, 0); while (!mStop) { MediaCodec.BufferInfo bufferInfo = new MediaCodec.BufferInfo(); int outputBufferIndex = mEncoder.dequeueOutputBuffer(bufferInfo, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_US); Log.d(TAG, "outputBufferIndex: " + outputBufferIndex); if (outputBufferIndex >= 0) { ByteBuffer outputBuffer = mEncoder.getOutputBuffer(outputBufferIndex); // write head info if (mVideoTrackIndex == -1) { Log.d(TAG, "this is first frame, call writeHeadInfo first"); mVideoTrackIndex = writeHeadInfo(outputBuffer, bufferInfo); } if ((bufferInfo.flags & MediaCodec.BUFFER_FLAG_CODEC_CONFIG) == 0) { Log.d(TAG, "write outputBuffer"); mMediaMuxer.writeSampleData(mVideoTrackIndex, outputBuffer, bufferInfo); } mEncoder.releaseOutputBuffer(outputBufferIndex, false); break; // 跳出循环 } } } private int writeHeadInfo(ByteBuffer outputBuffer, MediaCodec.BufferInfo bufferInfo) { byte[] csd = new byte[bufferInfo.size]; outputBuffer.limit(bufferInfo.offset + bufferInfo.size); outputBuffer.position(bufferInfo.offset); outputBuffer.get(csd); ByteBuffer sps = null; ByteBuffer pps = null; for (int i = bufferInfo.size - 1; i > 3; i--) { if (csd[i] == 1 && csd[i - 1] == 0 && csd[i - 2] == 0 && csd[i - 3] == 0) { sps = ByteBuffer.allocate(i - 3); pps = ByteBuffer.allocate(bufferInfo.size - (i - 3)); sps.put(csd, 0, i - 3).position(0); pps.put(csd, i - 3, bufferInfo.size - (i - 3)).position(0); } } MediaFormat outputFormat = mEncoder.getOutputFormat(); if (sps != null && pps != null) { outputFormat.setByteBuffer("csd-0", sps); outputFormat.setByteBuffer("csd-1", pps); } int videoTrackIndex = mMediaMuxer.addTrack(outputFormat); Log.d(TAG, "videoTrackIndex: " + videoTrackIndex); mMediaMuxer.start(); return videoTrackIndex; }} 四、调用示例
结合上一篇的解码器,可以做一些解码再编码的例子。
链接:
VideoDecoder mVideoDecoder = new VideoDecoder();mVideoDecoder.setOutputFormat(VideoDecoder.COLOR_FORMAT_NV12); // 设置输出nv12的数据VideoEncoder mVideoEncoder = null;// 某某线程中mVideoDecoder.decode("/sdcard/test.mp4", new VideoDecoder.DecodeCallback() { @Override public void onDecode(byte[] yuv, int width, int height, int frameCount, long presentationTimeUs) { Log.d(TAG, "frameCount: " + frameCount + ", presentationTimeUs: " + presentationTimeUs); if (mVideoEncoder == null) { mVideoEncoder = new VideoEncoder(); mVideoEncoder.init("/sdcard/test_out.mp4", width, height); } // yuv数据操作,例如保存或者再去编码等 mVideoEncoder.encode(yuv, presentationTimeUs); } @Override public void onFinish() { Log.d(TAG, "onFinish"); if (mVideoEncoder != null) mVideoEncoder.release(); } @Override public void onStop() { Log.d(TAG, "onStop"); if (mVideoEncoder != null) mVideoEncoder.release(); }}); 转载地址:http://xvru.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
netfilter应用场景
查看>>
netlink2.6.32内核实现源码
查看>>
Netpas:不一样的SD-WAN+ 保障网络通讯品质
查看>>
NetScaler的常用配置
查看>>
netsh advfirewall
查看>>
NETSH WINSOCK RESET这条命令的含义和作用?
查看>>
Netty WebSocket客户端
查看>>
netty 主要组件+黏包半包+rpc框架+源码透析
查看>>
Netty 异步任务调度与异步线程池
查看>>
Netty中集成Protobuf实现Java对象数据传递
查看>>
Netty事件注册机制深入解析
查看>>
Netty原理分析及实战(四)-客户端与服务端双向通信
查看>>
Netty和Tomcat的区别已经性能对比
查看>>
Netty客户端断线重连实现及问题思考
查看>>
Netty工作笔记0006---NIO的Buffer说明
查看>>
Netty工作笔记0007---NIO的三大核心组件关系
查看>>
Netty工作笔记0011---Channel应用案例2
查看>>
Netty工作笔记0013---Channel应用案例4Copy图片
查看>>
Netty工作笔记0014---Buffer类型化和只读
查看>>
Netty工作笔记0020---Selectionkey在NIO体系
查看>>